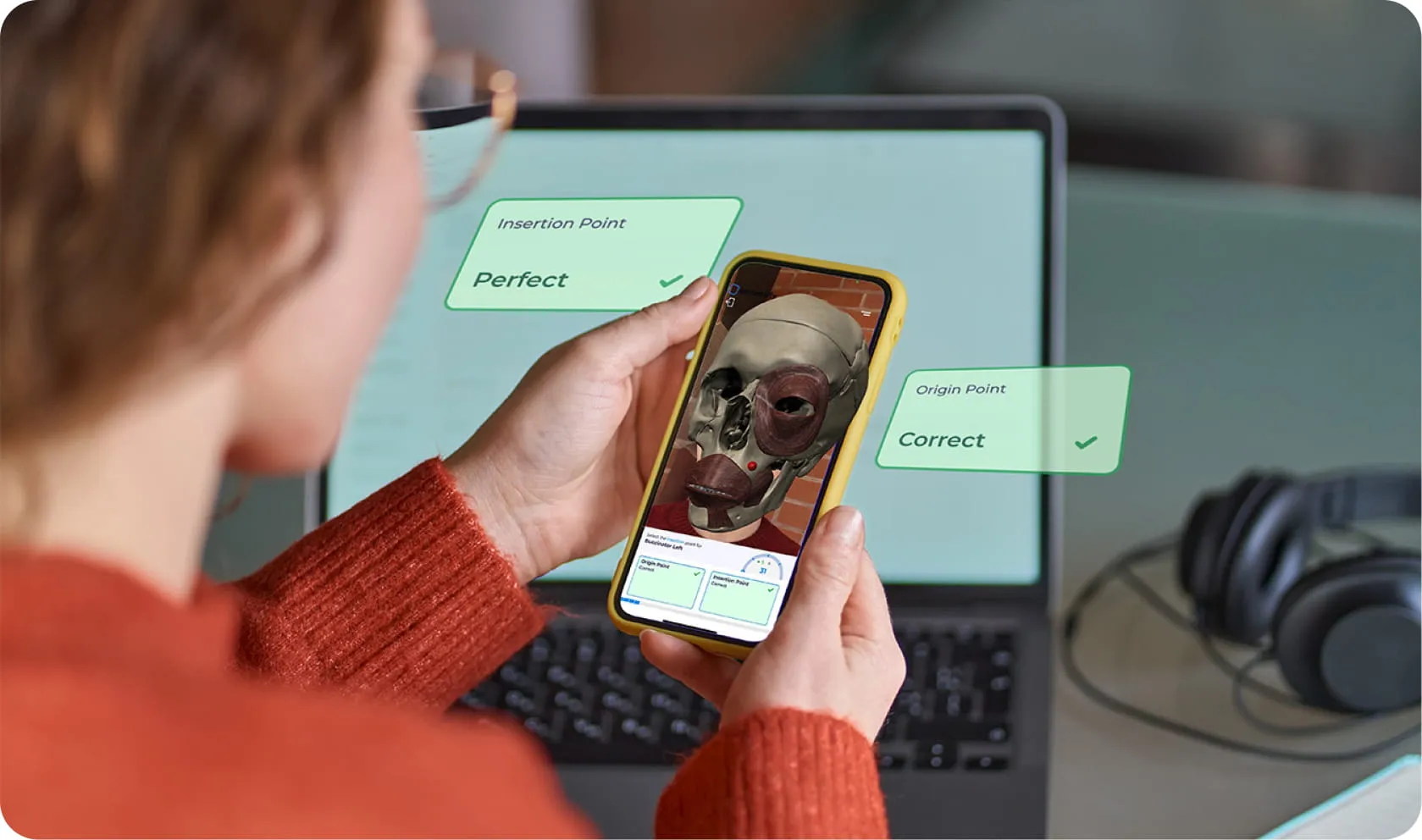
Embracing Digital Transformation in Healthcare Education Without Replacing Traditional Teaching

For university administrators looking to provide engaging healthcare education experiences that boost grades, support faculty, and meet student expectations, it can be hard to get a clear picture of how best to proceed.
On the one hand, a 2025 Frontiers in Education article suggests that the current generation of students prefer the personalization and interactivity that come hand-in-hand with digital learning technologies. This is unsurprising: we’re talking about digital natives, and it’s tempting to assume that those preferences point to a wholesale transition to tech-first approaches that leave offline teaching methods firmly in the past.
On the other hand, some reports—including data collated by the UK’s Higher Education Policy Institute and Unite Students—suggest that students overwhelmingly prefer face-to-face learning over independent or online study.
These positions aren’t as contradictory as they might seem. In fact, they suggest that today's healthcare students don't want either traditional or digital learning in isolation. Learners are looking for hybrid approaches that fuse the personal connection of in-person education with the flexibility and engagement of digital experiences.
Read on to discover:
- Some of the key advantages of digital learning in healthcare education
- The enduring (and evolving) role of in-person pedagogy
- How to strike the right balance between tradition and innovation
 What’s Driving the Shift Toward Interactive, Accessible and Simulation-Based Learning?
What’s Driving the Shift Toward Interactive, Accessible and Simulation-Based Learning?
There’s a reason colleges and other healthcare education institutions are adopting new learning technologies: they work. According to a 2024 literature review published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, medical simulations backed by VR and AR can have a range of positive impacts, including:
- Reductions in anxiety among student nurses who were able to practise clinical skills in VR simulations
- Increases in confidence among surgical students in dentistry with similar access to simulation technology
- Higher accuracy in marking dental implantation sites
As these examples suggest, healthcare education as a discipline is primed to reap the benefits of AR, VR, and similarly simulation-centric learning technologies. When students have the opportunity to gain more hands-on practise, improve their visualization techniques, and fail without negative repercussions, it’s no wonder researchers are seeing boosts to confidence and coordination.
And, in many ways, this is the tip of the AR/VR iceberg. The right educational technology tools can overlay digital content onto real-world environments, enabling students to interactively explore human anatomy, vital signs assessment, and procedural techniques. This immersive learning approach supports competency-based education and makes learning more engaging and practical. Even more simplistic eLearning techniques have been associated with significant knowledge gains, according to a 2025 contribution to BMC Medical Education.
In short: tech-assisted simulation is reshaping how clinical competency is developed, refined, and retained.
LEARN MORE ABOUT EDUCATION TECH | ‘Navigating the AI Landscape in Dental Education: Understanding Faculty Concerns and Student Motivations’
 Meeting Students’ Healthcare Education Expectations in the Digital Era
Meeting Students’ Healthcare Education Expectations in the Digital Era
If pedagogical efficacy is one side of the digital transformation coin, student expectations are the other. And here, too, there’s plenty of evidence in support of embracing digital practices in healthcare education.
Just a glance at McKinsey’s 2023 survey of over 7,000 higher ed students is enough to get a grasp on the digital preferences animating current cohorts. Today’s students are looking for:
- Easy, mobile-led user experience
- An omnichannel approach
- Asynchronous learning
- Multimedia resources
- Short, dynamic, and visual content
- Virtual reality and simulation
Clearly, these students would benefit from the kinds of AR- and healthcare simulation-led tooling described above. But, once again, this understanding of students’ digital preferences is only part of the story. McKinsey’s data equally points to a swathe of entirely legitimate factors that dissuade students from opting for fully remote, digital-only programs, including a preference for the discipline and structure traditional methods employ. And, tellingly, one of the most cited considerations was a desire for access to teachers. So, while students are asking for more technology, they're also asking for a more integrated, responsive, and human-centered educational experience.
In short: traditional teaching still matters. And that same sentiment applies even when we’re talking about the effectiveness of digital teaching tools. The BMC Medical Journal article makes this point: the authors are quick to note that while participants did show improved knowledge gain, the digital tools used in the study were an addition to the traditional curriculum, as opposed to a substitution.
The implications here are clear: digital tools serve as an enhancement rather than a replacement for in-person learning.
MORE FROM THE BLOG | ‘Bridging the Gap: What Dental Schools Can Learn from Medical Education Technology Trends’
How Do Institutions Strike the Balance Between Digital and Human Interaction?
While digital tools and practices (especially around AR, VR, and app-based simulations) are revolutionizing healthcare education, this process shouldn't come at the expense of traditional learning.
Faculty members remain essential in guiding students and developing interpersonal skills. That’s particularly worth remembering in the context of healthcare education, which places a real emphasis on ensuring the ethical and compassionate treatment of patients. Real-world interactions with educators, peers, and patients are essential for practising communication and professional empathy: key clinical skills that can’t be lost in the excitement of digital transition.
Given the irreplaceability of the in-person elements of healthcare education, a dependence on traditional practices to secure digital improvements, and student expectations of a hybrid approach, the challenge lies in ensuring an effective transition.
This requires:
- Identifying the appropriate phase in the healthcare curriculum to introduce digital technologies
- Evaluating which traditional techniques should be retained or replaced
- Determining which disciplines should integrate specific digital content for optimal learning outcomes
- Supporting faculty in onboarding and adapting to digital teaching methodologies
KEEP READING | ‘Why Dental Education Needs a Tech-Driven Revolution’
The Key Takeaway: Preparing for the Future of Healthcare Education
The digital transformation in healthcare education is still in its early stages, and there are currently no universal standards for the application of digital tools. However, as institutions strive to enhance their curricula, the most learner-centered and forward-thinking healthcare programs will be those that integrate innovative digital resources while maintaining strong faculty-led teaching practices.
By utilizing interactive and accessible learning tools, healthcare educators can support student expectations, which in turn allow institutions to reach new heights of student attainment and satisfaction.
The future of healthcare education depends on a balanced approach: one that interweaves new technologies with the human connection at the core of hands-on practice and patient-centered care.
Looking to Supplement Your Curriculum with Simulation Software?
Reach out to our experts today to find out how.
Join our mailing list
Get the latest updates on immersive learning, industry trends, and resources delivered straight to your inbox.